Fatty Liver and Diabetes
Fatty Liver and Type 2 Diabetes
Fatty liver and diabetes are two common health conditions that often go hand in hand, affecting millions of people worldwide. Both diseases have significant implications for overall health and quality of life, and their interconnected nature makes managing them a complex but essential task.
In this blog, we will explore the connection between fatty liver and diabetes and discuss strategies for prevention.
What is a Fatty Liver?
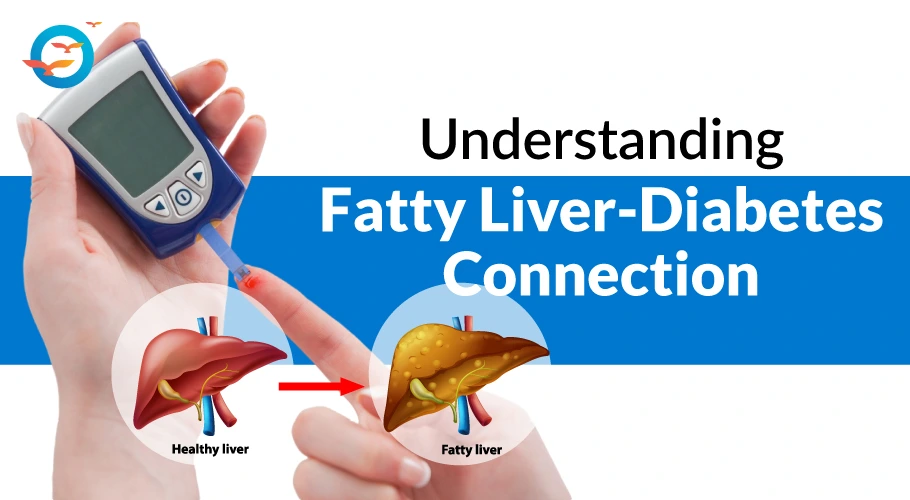
A fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, happens when too much fat builds up in liver cells. This can be due to factors like heavy alcohol use, obesity, insulin resistance, and some medications.
Too much fat can inflame the liver, causing damage and leading to serious conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or cirrhosis. Often, fatty liver shows no clear symptoms, making medical tests essential for diagnosis.
Why is it important to have a Healthy Liver?
Keeping your liver healthy is vital for overall well-being because it performs many essential functions. It detoxifies harmful substances, processes nutrients, produces bile for digestion, and stores vitamins and minerals.
A healthy liver also helps regulate blood sugar, metabolizes fats and proteins, and supports the immune system. When the liver is damaged, these important processes can be disrupted, leading to health problems like diabetes, increased infections, and severe conditions like cirrhosis or liver failure.
The occurrence of fatty liver in men, women, and particularly in diabetics
The prevalence of fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, varies among different groups. Men generally have a higher rate of fatty liver than women, due to differences in fat distribution, lifestyle, and hormones. However, postmenopausal women have an increased risk due to hormonal changes.
Among people with diabetes, the prevalence is much higher, often over 50%, because of the link between insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Diabetics are also more likely to develop severe forms of fatty liver disease, like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure if not managed.
Relation Between Fatty Liver and Diabetes
For people with diabetes, it's crucial to overcome fatty liver because these conditions are closely linked and affect overall health. Fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, worsens insulin resistance, making blood sugar management harder. This can lead to poor blood sugar control and increase the risk of complications like heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
The good news is that fatty liver can be reversed, especially if caught early. By making lifestyle changes, such as improving diet and exercising, individuals can reduce liver fat and restore normal liver function.
Tips for Reversing Fatty Liver:
Key strategies for reversing fatty liver include adopting a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while reducing the intake of saturated fats, refined sugars, and alcohol. Regular physical activity is also crucial, as it helps improve metabolism and reduce liver fat.
Weight loss is particularly effective, with even modest reductions in body weight leading to significant improvements in liver health. Additionally, managing underlying conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol through medication and lifestyle modifications can further aid in reversing fatty liver.
Recommended:
To support liver health, include foods such as beetroots, garlic, ginger, and green tea in your diet. Also beneficial are sources of essential fats like avocados, walnuts, and various colorful berries.
Important:
Certain herbs, like milk thistle, ginseng, and licorice, may be beneficial, but should only be consumed under professional guidance.
Avoid:
It's best to avoid deep-fried foods, trans fats, and red meat, as they can harm liver health. Additionally, steering clear of alcohol and alcoholic beverages is crucial for maintaining a healthy liver.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fatty liver and diabetes are closely linked and can make each other worse. Fatty liver can increase insulin resistance, making diabetes harder to manage and raising the risk of complications like heart disease and liver damage.
The good news is that fatty liver can be reversed. By adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing weight, people can improve their liver health and overall metabolism. Early intervention is key to preventing the progression of fatty liver in diabetics. By focusing on liver health, individuals can better control their blood sugar and reduce the risk of serious complications, leading to a healthier life.
At FFD, we assist people in not only reversing diabetes but also in losing weight and enhancing overall health, which in turn helps in reversing fatty liver.
Stay healthy... be happy
FAQs
Can fatty liver cause diabetes?
Yes, fatty liver worsens insulin resistance, increasing the risk of developing diabetes or making diabetes harder to manage.
How can I reverse fatty liver naturally?
I can reverse fatty liver by maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, losing excess weight, and avoiding alcohol and processed foods.
What foods should I avoid for fatty liver and diabetes?
I should avoid fried foods, trans fats, refined sugars, alcohol, and red meat to improve liver health and blood sugar control.
Can losing weight help with fatty liver?
Yes, even a small weight loss of 5-10% can significantly reduce liver fat and improve overall health.
How does fatty liver affect my blood sugar levels?
Fatty liver increases insulin resistance, making it harder to control blood sugar levels and raising the risk of diabetes complications.